See also


 16.05.2025 11:00 AM
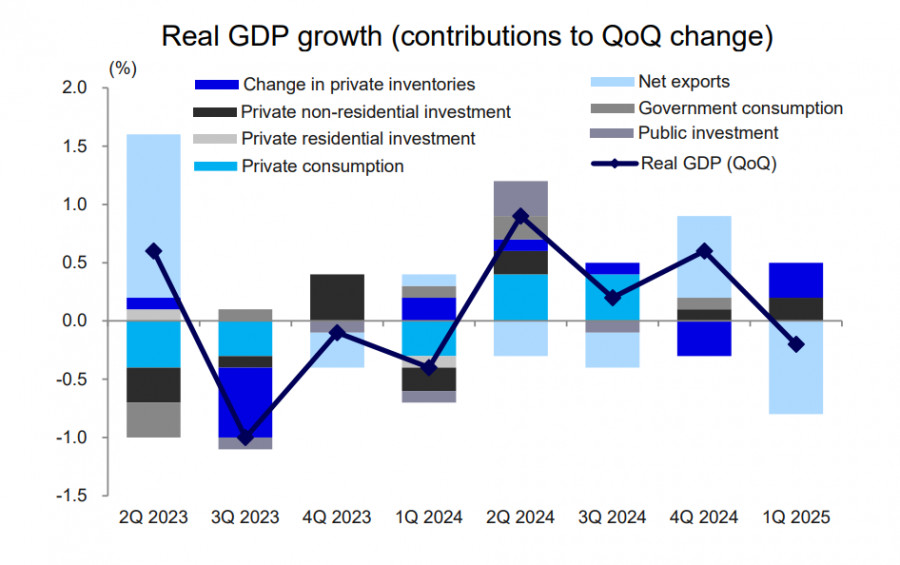
16.05.2025 11:00 AMThe GDP report published on Thursday revealed that Japan's economy contracted by 0.7% year-over-year in the first quarter—its first annual decline in the past year and significantly worse than expected.
The contraction is primarily attributed to U.S.-imposed trade tariffs and a decline in exports. However, the report also clearly indicated stagnation in private consumption, suggesting that the economy had already begun losing support from external demand even before Trump's April 2 announcement of sweeping "reciprocal" tariffs.
Japan's economy is highly dependent on external demand, and if tariff negotiations fail to produce positive outcomes, the downturn could deepen in the second quarter—something markets would likely interpret as the official onset of a recession.
As usual, the situation presents a challenge for the Bank of Japan. On the one hand, noticeable wage growth achieved through union pressure is a positive for boosting consumer demand. On the other hand, it also drives inflation higher, thus increasing the need to raise interest rates.
The yen strengthened in response to the GDP report. The unique structure of Japan's economy means that a slowdown leads to reduced raw material imports (on which Japan is heavily dependent), thereby lowering supply. At the same time, the need to contain inflation implies higher BoJ rates and yields—factors that continue to support demand for the yen and remain key in forecasting its trajectory.
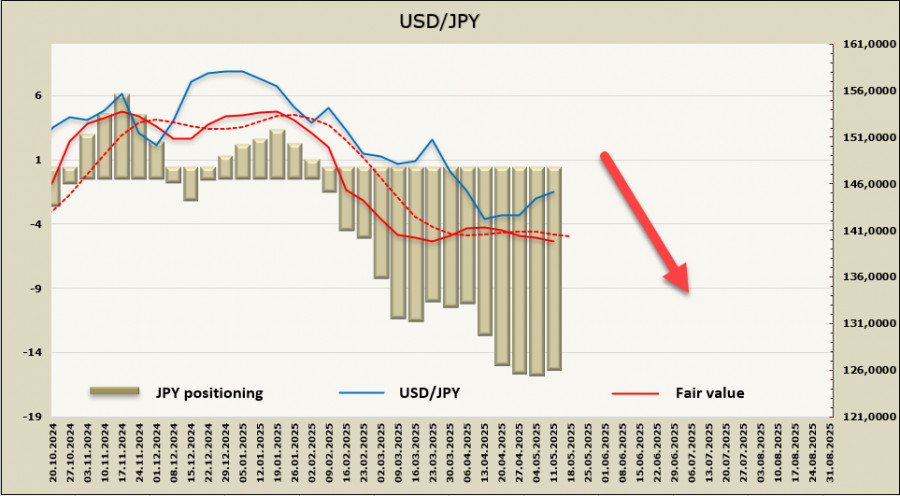
The net long position on the yen saw a slight correction to +15.52 billion, maintaining a strong bullish speculative bias. The estimated fair value has again fallen below the long-term average and continues to trend downward.
We had anticipated a resumption of the USD/JPY decline last week. However, the correction gained strength following the announcement of a tariff agreement between the U.S. and China, which temporarily boosted risk appetite and weakened the yen. Nonetheless, the long-term outlook remains unchanged. Slowing inflation in the U.S. puts downward pressure on yields, as the Fed may become more aggressive with rate cuts, whereas the Bank of Japan has little choice but to gradually unwind the effects of Abenomics through policy tightening.
We expect the bearish trend to continue, with the nearest support zone at 141.00–141.20. At this stage, a deeper decline is possible but too early to confirm.
You have already liked this post today
*The market analysis posted here is meant to increase your awareness, but not to give instructions to make a trade.